
All Solutions
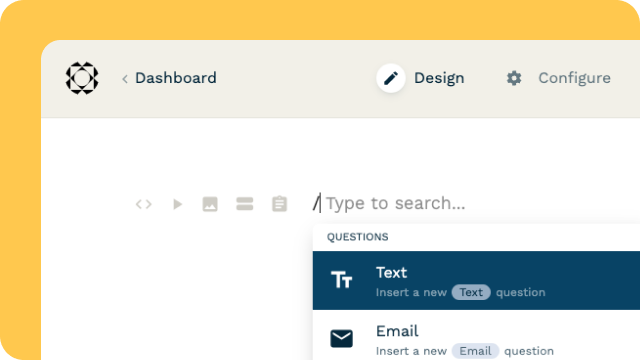
Explore all the solutions you can create with Paperform: surveys, quizzes, tests, payment forms, scheduling forms, and a whole lot more.
See all solutions






Connect with over 2,000 popular apps and software to improve productivity and automate workflows
See all integrationsSolutions
All Solutions

Explore all the solutions you can create with Paperform: surveys, quizzes, tests, payment forms, scheduling forms, and a whole lot more.
See all solutionsIntegrations

Connect with over 2,000 popular apps and software to improve productivity and automate workflows
See all integrationsResources
Data collection methods: Types and examples

Leveraging the right data can be a game-changer for any business or individual seeking success. But how do you sift through the myriad of data collection methods to find what works best for you? .
Whether you're looking to engage more authentically with your customers or an academic researcher on the brink of a breakthrough, we've got you covered, with this guide to data collection methods.
What is data collection?
Let's get down to basics: what exactly is data collection? Well, imagine you're planning a party and you want to know what kind of food your guests would like. You would probably ask them, right? That's data collection in its simplest form— gathering information to help you make decisions.
In a broader sense, data collection is the process of gathering and measuring information on variables of interest, in a systematic fashion. This enables someone to answer relevant questions and evaluate outcomes.
In the business world, this could involve collecting customer feedback to improve a product, gathering market research to understand trends, or compiling sales data to inform strategy.
The 'data' you collect can take many different forms - numbers, words, images, and so on. It could be:
- Qualitative (describing qualities or characteristics, like the color of a product)
- Quantitative (expressing a certain quantity, amount, or range, like the number of users on a website).
There are many ways to categorize types of data. As well as being categorized by data type, it can also be broken down by how that data is collected:
- First Party Data: This is data you collect directly from your own audience or customers. It's generally the most accurate and reliable.
- Second Party Data: This is data collected by someone else that you have access to. It's essentially someone else's first party data.
- Third Party Data: This is data collected by an entity that doesn't have a direct relationship with the data subject. It’s often aggregated from various sources and sold to other parties, which may prompt businesses or individuals to consider using a data removal service to manage and protect their digital information from widespread distribution.
Why is data collection important?
Now that we understand what data collection is, you might be wondering, "Why is it so important?"
Well, imagine trying to hit a target with your eyes closed. Pretty hard, right? That's what making decisions without data is like—you're making guesses without really knowing what's going on.
Data collection is like opening your eyes before taking the shot. It provides the insights and evidence needed to make informed decisions, rather than simply guessing. Whether you're trying to improve your product, understand your customers better, or make strategic business decisions, data collection is the key that unlocks the door to knowledge.
Here's why data collection is so important:
- Informing decision making: With accurate data, you can make decisions based on facts, not just assumptions. This reduces risk and can lead to better outcomes.
- Understanding trends and patterns: Collecting data over time can help you identify trends, patterns, and changes in your business or market. This can help you stay ahead of the game.
- Measuring performance: Data can help you track progress, measure results, and see if you're meeting your goals. It's a way of keeping score in the game of business.
- Improving processes and products: By collecting data on your products, services, or processes, you can identify what's working well and what needs improvement.
- Understanding your audience: If you want to serve your customers or audience effectively, you need to understand them. Data collection can help you get to know their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
So, whether you're running a business, conducting research, or just trying to make better decisions, data collection is a crucial tool in your toolbox.
With Paperform, collecting data has never been easier
Start your 14-day free trial now. No credit card needed.
Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data can be gathered using various methods, which can be broadly categorized into qualitative and quantitative approaches. Let's break down these methods:
Qualitative Data Collection Methods
Qualitative methods provide depth and detail through direct conversation or observation. They don't involve numerical data but instead seek to understand concepts, experiences, and interactions.
Here are some qualitative primary data collection methods:
- In-depth interviews: These are one-on-one conversations where detailed information is gathered about an individual's experiences, behaviors, attitudes, and perceptions.
- Focus groups: These are guided group discussions that gather collective views and experiences on a certain topic.
- Observations: This method involves watching and recording behaviors, events, or actions, often in a natural setting.
- Case Studies: These are detailed investigations of a single individual, group, or event, where various data sources may be used.
Quantitative Data Collection Methods
Quantitative methods, on the other hand, involve numerical data that can be quantified and statistically analyzed. They often seek to measure or compare data. Here are some quantitative primary data collection methods:
- Surveys: These are used to gather data from a large number of respondents using a structured questionnaire with specific, predetermined questions.
- Experiments: These involve manipulating one or more variables to determine their effect on another variable.
Choosing between qualitative and quantitative methods, or a mix of both, depends on your research objectives, your resources, and the nature of the data you're seeking to collect.
Secondary data collection methods
While primary data collection involves gathering new data directly from the source, secondary data collection, on the other hand, makes use of data that already exists. It's like using a recipe book to cook a meal—someone else has done the work of compiling the ingredients and instructions, and you're putting it to use.
This data is often used to supplement primary data or to gain a broader understanding of a research topic. Here are some common sources of secondary data:
- Government records: Government agencies collect a vast amount of data on various subjects like economics, population demographics, health, and more. These records are usually available to the public and can be a rich source of information.
- Academic publications: Academic journals and theses often contain detailed research data. These publications go through rigorous peer review, so the data is generally reliable.
- Industry reports: Many industries publish reports that contain data about market trends, consumer behavior, and more. These reports can be particularly useful for businesses.
- Media sources: Newspapers, magazines, and online media platforms often publish data on a wide range of topics.
- Online databases: There are many online databases that aggregate and organize data on various topics. Some are free to use, while others require a subscription.
- Internal company records: If you're researching a topic related to your own business, don't forget about your internal data. Sales records, customer databases, and past research reports can all be valuable sources of secondary data.
Remember, while secondary data can be a valuable resource, it's also important to evaluate the quality and relevance of the data to ensure it meets your needs.
With Paperform, collecting data has never been easier
Start your 14-day free trial now. No credit card needed.
Common data collection methods for businesses
Businesses are heavily reliant on data to make informed decisions. Here's a look at common data collection methods:
Surveys
Businesses often use surveys to gather feedback from customers about their products or services. These can be conducted via email, on a website, through social media, or in person.
Customer interviews
One-on-one interviews with customers can provide in-depth insights into customer experiences, preferences, and pain points.
Sales data
Analyzing sales data can uncover trends, performance, and customer purchasing habits. Paperform can be a part of this process, linking forms to sales and monitoring platforms.
Website analytics
Tools like Google Analytics can track customer behavior on a website, providing valuable data on things like how customers found the site, which pages they viewed, how long they stayed, and more.
Social media monitoring
Social media platforms provide a wealth of data on customer opinions, trends, and competitor activity. Monitoring these platforms can provide real-time insights that are highly relevant to marketing and product development.
Third-party data
Many businesses purchase data from third-party providers to supplement their own data. This can include demographic data, market research data, or industry benchmark data.
Choosing the right data collection method often depends on what question you're trying to answer, what resources you have available, and what kind of data you need. With the right approach, data collection can provide powerful insights that drive business growth.
Sampling methods in data collection
When it comes to data collection, obtaining insights from an entire population is often impractical or even impossible. That's where sampling methods come into play.
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of individuals or elements from a larger population to gather data and make inferences about the whole. By carefully selecting and studying a representative sample, researchers can gain insights that reflect the characteristics of the entire population.
There are several common sampling methods used in data collection:
1. Random sampling
In this method, every individual or element in the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample. Random sampling helps ensure that the sample is unbiased and representative of the population as a whole.
2. Stratified sampling
With stratified sampling, the population is divided into distinct subgroups or strata based on specific characteristics. Then, a random sample is selected from each stratum in proportion to its size. This method allows researchers to ensure representation from different subgroups within the population.
3. Cluster sampling
Cluster sampling involves dividing the population into clusters or groups, often based on geographic proximity. Researchers then randomly select clusters and collect data from all individuals within the chosen clusters. Cluster sampling can be more practical and cost-effective when the population is large and dispersed.
4. Convenience sampling
Convenience sampling involves selecting individuals who are easily accessible or readily available. While this method is convenient, it may introduce bias, as it may not accurately represent the entire population. Convenience sampling is often used in exploratory or preliminary research.
5. Purposive sampling
Purposive sampling involves deliberately selecting individuals who meet specific criteria or have certain characteristics. This method is commonly used in qualitative research when the focus is on studying a particular group or capturing diverse perspectives.
Data collection and lead generation
Data collection and lead generation go hand in hand. Like a detective gathering clues to solve a case, businesses collect data to find potential customers—valuable leads that could transform into interest into sales and sales into growth.
Lead generation is all about attracting and converting strangers and prospects into leads—people who have shown interest in your company's product or service. It's like fishing: you cast your rod and hope to reel in some fish.
The more effectively you can target your audience, the more likely you are to catch the right fish. And that's where data collection comes in.
When it comes to lead generation, this could involve collecting data on potential customers' needs, habits, preferences, and behaviors. This data can be collected through various methods such as online forms, surveys, social media interactions, website analytics, and more.
Using Paperform, for example, you can create engaging and customized forms to capture leads. You can ask for the typical contact information like name, email, and phone number, but you can also dive deeper.
Want to know what products they're interested in? Or how they heard about your business? You can collect all this data and more. Then analyze it in-app, or use an integration to send the data to an app like Google Sheets to dive deeper.
Once you've gathered this data, you can use it to in multiple ways to improve your business, including:
- Refining marketing strategy: Understanding customer preferences to target advertising more effectively.
- Personalizing communication: Tailoring messages based on individual customer interests and history.
- Improving website experience: Utilizing user behavior to optimize website design and usability.
- Identifying product trends: Analyzing sales data to determine popular products and potential new offerings.
- Optimizing pricing strategy: Evaluating market and competitor pricing to position products competitively.
- Managing reputation: Monitoring social media and online reviews to address customer concerns promptly.
It's simple: the more you know about your leads, the better you can meet their needs and build lasting relationships.
With Paperform, collecting data has never been easier
Start your 14-day free trial now. No credit card needed.
Paperform: Your key to informed decision-making
Harnessing the power of data doesn't have to be a daunting task. With Paperform, you've got a simple yet powerful tool at your fingertips, perfect for collecting all kinds of data.
Paperform is more than just an online form builder—it's a versatile platform that allows you to design beautiful forms, surveys, quizzes, and more. It's as easy as writing a doc, and with more than 20 question types, there's no limit to the kind of data you can collect.
Want to collect customer feedback? Need to do a quick market research survey? Easy as pie. From simple text responses to more complex data like ratings, dates, and even file uploads, Paperform has got you covered.
But it's not just about collecting data. With Paperform you can send that data anywhere you need it. Integrate directly or with over 3,000 apps through Make and Zapier, or export your data to Microsoft Excel.
Whether you're a small business owner looking to understand your customers better, a teacher wanting to assess student learning, or a researcher gathering data for a project, Paperform is a powerful ally. It's versatile, it's easy to use, and it's designed to make data collection a breeze.
So why wait? Dive into the world of data collection with Paperform and discover the insights you need to make informed decisions. Start your free trial today and experience the power of intuitive data collection with Paperform.
Related reading
Deepak (Dee) Shukla, the dynamic founder of Pearl Lemon, built the leading SEO agency in London by l...
Here is the ultimate list of online form builders, what they do best, their pricing, and examples to...
When Luiz Sifuentes lost the platform powering his entire web design business, he rebuilt smarter—wi...
All of our product updates and big company news for Paperform and Papersign from Oct 24 - May 25 to ...